Downloadable
ABC Segmentation , what it is and how to implement it
In supply chain management, identifying key elements that require special attention can make the difference between success and failure.

In supply chain management, identifying key elements that require special attention can make the difference between success and failure. A tool that can help you identify these key elements is ABC segmentation.
In this manual, we will explore how you can optimize your supply chain using ABC segmentation combined with the Pareto principle, and how our specially designed Excel template can be your ally for implementing it effectively (download the template here). Additionally, we will show you different strategies for each product classification.
What is ABC Segmentation?
ABC segmentation is a classification technique that divides products or customers into different categories based on their relative importance. It is based on the Pareto principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, which states that approximately 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. In the context of supply chain management, this means that a minority of products or customers will generate the majority of revenue or issues.
By understanding which products generate the most revenue or which customers have a significant impact on your operations, you can allocate resources appropriately and make data-driven decisions. This leads to greater efficiency, better inventory allocation, and improved customer satisfaction.
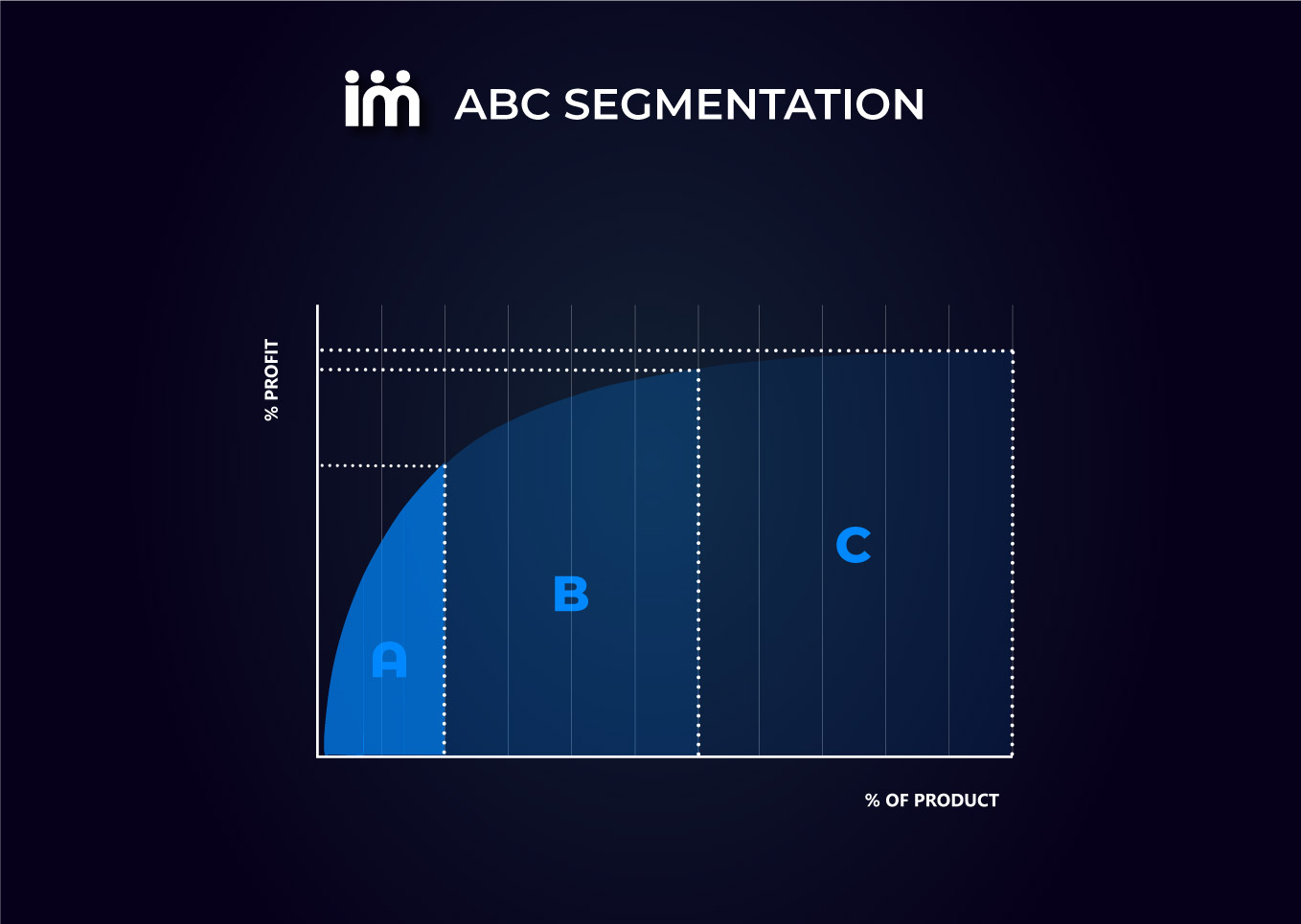
ABC Segmentation Applied to Supply Chain
Applying ABC segmentation to the supply chain is particularly useful for identifying and classifying our products based on the impact they have on our business. ABC segmentation divides our products into three main categories:
- Class A: Products of highest importance and value, representing 80% of the accumulated value. Focusing your attention on this category will allow you to allocate the appropriate resources to maximize their performance and optimize your results.
- Class B: Products of moderate importance, representing an intermediate percentage of the total value; approximately 15% of the accumulated value. While not as critical as Class A, they still require proper management to ensure efficient operation.
- Class C: Items of least importance fall into this category, representing approximately 5% of the accumulated value. Managing them more simplistically will allow you to free up resources for the more critical categories.
Types of ABC Segmentation:
Additionally, ABC segmentation can classify products based on different criteria:
- Sales volume.
- Cost of goods.
- Profit margin.
Other Classifications of ABC Segmentation:
In ABC segmentation, we can also establish a classification of our products based on their storage cost. With this data, we can determine the cost of holding a unit of these products in stock for one day. This type of classification will allow us to identify products with higher storage costs to optimally adjust our inventory levels.
What Strategies to Follow for Each ABC Product Category?
Below, we detail different strategies for each of the product classifications we can perform using ABC segmentation.
Strategies for Products Categorized as A:
- Prioritize availability and delivery time: Since Class A products generate the majority of your revenue, it is crucial to ensure they are always available to your customers. Maintain strict control over inventory levels, implement agile replenishment strategies, and establish solid agreements with your suppliers to ensure a steady flow of supplies. Additionally, focus your efforts on reducing delivery times, as speed is a priority for these products.
- Customize the service: Class A products are usually those with high demand and are preferred by your customers. To meet their specific needs, consider offering personalized services such as expedited shipping, customization options, or specialized technical support. This will strengthen your relationship with your customers and keep them loyal to your company.
- Establish strategic pricing policies: Since Class A products are highly profitable, you might consider setting differentiated pricing policies to maximize your profit margins. This can include strategies like premium pricing, exclusive discounts for repeat customers, or value-added bundles combining several Class A products. Conduct profitability analysis and closely monitor demand and market changes to adjust your prices optimally.
Strategies for Products Categorized as B:
- Optimize inventory management: Class B products do not generate as much revenue as Class A, but they are still important for your business. Carefully track inventory levels of these products and apply demand forecasting techniques to avoid stockouts or excess inventory. Consider strategies such as scheduled replenishment or just-in-time to maintain an appropriate balance.
- Implement upselling and cross-selling strategies: Leverage the established relationship with your customers who purchase Class B products to offer related or higher-value products. Use upselling and cross-selling techniques to increase the average purchase value and maximize the revenue generated from these customers.
- Offer promotional incentives: To stimulate demand for Class B products, consider implementing discount programs, promotions, or special packages. This will help attract potential customers and encourage the purchase of these products in particular.
Strategies for Products Categorized as C:
- Profitability analysis: Conduct a thorough profitability analysis of Class C products. While these products may have a low impact on your total revenue, it is important to understand if they are generating losses or affecting your profit margin. If you identify unprofitable products, consider reducing their presence in your inventory or reevaluating their marketing strategy.
- Liquidation or discontinuation strategies: If Class C products do not meet your business goals or have very low demand, you might consider liquidation or discontinuation strategies. This involves reducing prices and conducting promotional sales to clear out existing inventory. If demand remains low and no significant change is expected, you may decide to stop offering those products and focus your resources on more profitable items.
- Supply chain optimization: For Class C products, it is important to optimize costs and efficiency in the supply chain. Examine processes and look for opportunities to reduce production, storage, and distribution costs. Consider seeking more cost-effective suppliers or consolidating shipments to minimize transportation expenses. Additionally, ensure you maintain adequate inventory and avoid excesses that may incur unnecessary costs.
- Market research: Conduct market research to better understand the reasons behind the low demand for Class C products. It may be useful to identify changing market trends, customer preferences, or competition. This information will help you make informed decisions about how to improve or replace existing products in this category.
In summary, for Class A products, prioritize availability, personalized service, and strategic pricing policies. For Class B products, optimize inventory management, implement upselling and cross-selling strategies, and offer promotional incentives. For Class C products, analyze profitability, consider liquidation or discontinuation strategies, optimize the supply chain, and conduct market research to make informed decisions.
Advantages of Using the ABC Segmentation Excel Template
To help you implement ABC segmentation and optimize your supply chain, we have developed an Excel template that will guide you through the process. By opening our template, you will get:
- Automated analysis: Our template will perform the necessary calculations to classify your products into A, B, and C categories based on their importance and value.
- Clear visualization: The template will visually show how your products are distributed in each category, allowing you to quickly identify those requiring special attention.
- Informed decision-making: With the segmentation clearly defined in the template, you can make decisions based on concrete data, allocating resources and efforts more effectively.
How to Use Our ABC Segmentation Excel Template
In the Data Source tab, load sales, amount, or profit margin according to the analysis you want to perform. Enter the product code, and the description if you are more familiar with working with your product names. Compute these data on a monthly basis, for the last 13 months; if you do not have information for the last month, substitute it with this month’s forecast.
In the ABC summary, you can filter and sort references and observe the percentage each reference contributes to the total.
In the ABC chart tab, you can modify your ABC parameters (although we recommend 80/95/100) and visually observe the distribution that follows your business, such as the number of references belonging to each category at a glance.
At Imperia, we work to democratize the use of supply chain management platforms by offering personalized solutions that enable companies to optimize their demand planning, production, and purchasing processes. Through our Supply Chain Planning software, we make supply chain management more accessible to all companies. Don’t wait any longer and

Enter your email and download the content
In supply chain management, identifying key elements that require special attention can make the difference between success and failure.


