Downloadable
ABC/XYZ Segmentation, the Ultimate Combination for Your Supply Chain
ABC and XYZ segmentation is based on classifying references according to their relevance and frequency of use, respectively.

In previous articles, we have discussed two types of segmentation: ABC segmentation and XYZ segmentation. Both methodologies were particularly useful when applied to our company's supply chain, allowing us to manage it more efficiently. But what would happen if we combined both methodologies in supply chain management? Today, we introduce the ABC-XYZ segmentation!
In this article, we will show how ABC-XYZ segmentation can be a powerful tool to optimize any company's supply chain. Additionally, we will present our specially designed Excel template to simplify the implementation of this strategy in your business, allowing you to enter your own references and obtain a clear and precise segmentation according to ABC-XYZ criteria. Let's get started!
ABC-XYZ Segmentation: The Perfect Combination
ABC and XYZ segmentation are based on classifying references according to their relevance and frequency of use, respectively. To achieve optimal classification, it is important to establish ranges that clearly differentiate between the various categories.
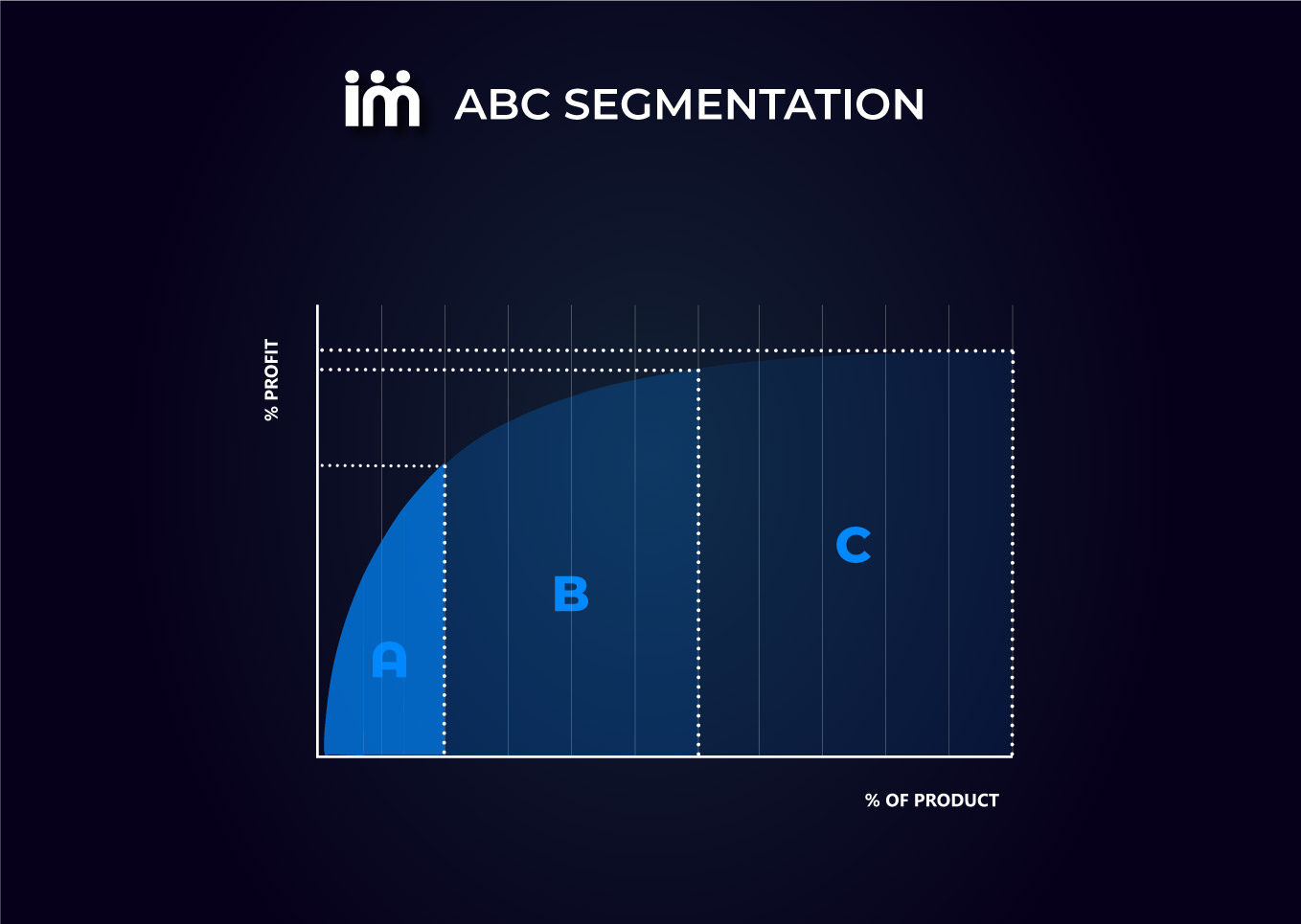
For ABC segmentation, the optimal ranges are based on the Pareto principle, also known as the 80/20 rule. According to this principle, approximately 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. In the context of reference classification, this translates to the following ranges:
- Class A: The top 20% of references that account for 80% of the accumulated value (usage, demand, or importance).
- Class B: The next 15% of references that represent 15% of the accumulated value.
- Class C: The remaining 65% of references that account for 5% of the accumulated value.
These ranges allow for a clear differentiation between references of high, medium, and low importance.
For XYZ segmentation, the optimal ranges are:
- Class X: References with a coefficient of variation (CV) less than or equal to 0.5. These references have stable and predictable demand or frequency of use.
- Class Y: References with a CV greater than 0.5 and less than or equal to 1.5. These references exhibit moderately variable demand or frequency of use.
- Class Z: References with a CV greater than 1.5. These references have highly variable and unpredictable demand or frequency of use.
These ranges help distinguish between references with constant, moderately variable, and unpredictable usage, thus facilitating more efficient and needs-adapted information management.
Implementing ABC-XYZ Classification
In implementing ABC-XYZ segmentation, it is particularly interesting to combine six months of historical data with six months of forecasts. This achieves a balance between recent real information and future projections, providing a more complete and contextualized view of the situation.
On one hand, six months of historical data provide valuable insights into trends and patterns that have emerged, offering a solid basis for analysis. On the other hand, incorporating six months of forecasts anticipates potential changes, events, and emerging trends, which facilitates informed decision-making and adaptation to a constantly evolving environment.
Together, this combination of historical and projected information offers an enriching and effective perspective for addressing and improving information management in any field.
It is also important to note that by summing the amount, quantity, or margin over six months, we are eliminating the effect of seasonality for ABC calculation. Analyzing a shorter period would give higher weight to products with peak sales during the selected period, while those with a valley period would be underestimated.
As mentioned in the XYZ segmentation article, the more historical data we have for a reference, the more precise its decomposition will be, and we will be able to understand what part of its variability is due to seasonality and cycles, and which part is more complex to predict. However, for an initial analysis, this is sufficient, although for a more thorough analysis, we recommend considering all available historical data.
Calculating ABC-XYZ Segmentation: Quantity, Value, and Margin
When calculating ABC-XYZ segmentation, different criteria can be used to classify references, such as quantity, value, or margin. Each of these approaches has its own characteristics and may be more suitable depending on the context or objective of the segmentation.
- Quantity: ABC-XYZ segmentation based on quantity focuses on the frequency of use or demand for references. This approach is useful when classifying references according to their popularity or demand level. For example, in libraries and documentation centers, this criterion can help identify and prioritize the most requested references by users, ensuring they are available and accessible.
- Value: Using value as a criterion for ABC-XYZ segmentation involves classifying references according to their economic value. This approach is useful in contexts where the cost of acquiring, maintaining, or storing references is a critical factor in information management. In this case, references with higher economic value might receive higher priority in terms of resource allocation and space, while those with lower value might be considered less critical.
- Margin: ABC-XYZ segmentation based on margin focuses on the profitability of references. This criterion is especially relevant in commercial or sales environments, where the main goal is to maximize profitability. By classifying references based on their margin, one can identify and prioritize those that generate higher profits, which can help optimize resource allocation and decision-making based on profitability.
Each of these approaches has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the appropriate criterion will depend on the context and objectives of ABC-XYZ segmentation. It is important to carefully evaluate the needs and priorities of the organization when deciding which criterion to use to ensure effective and aligned information management.
Characteristics of Each Group in ABC-XYZ Segmentation:
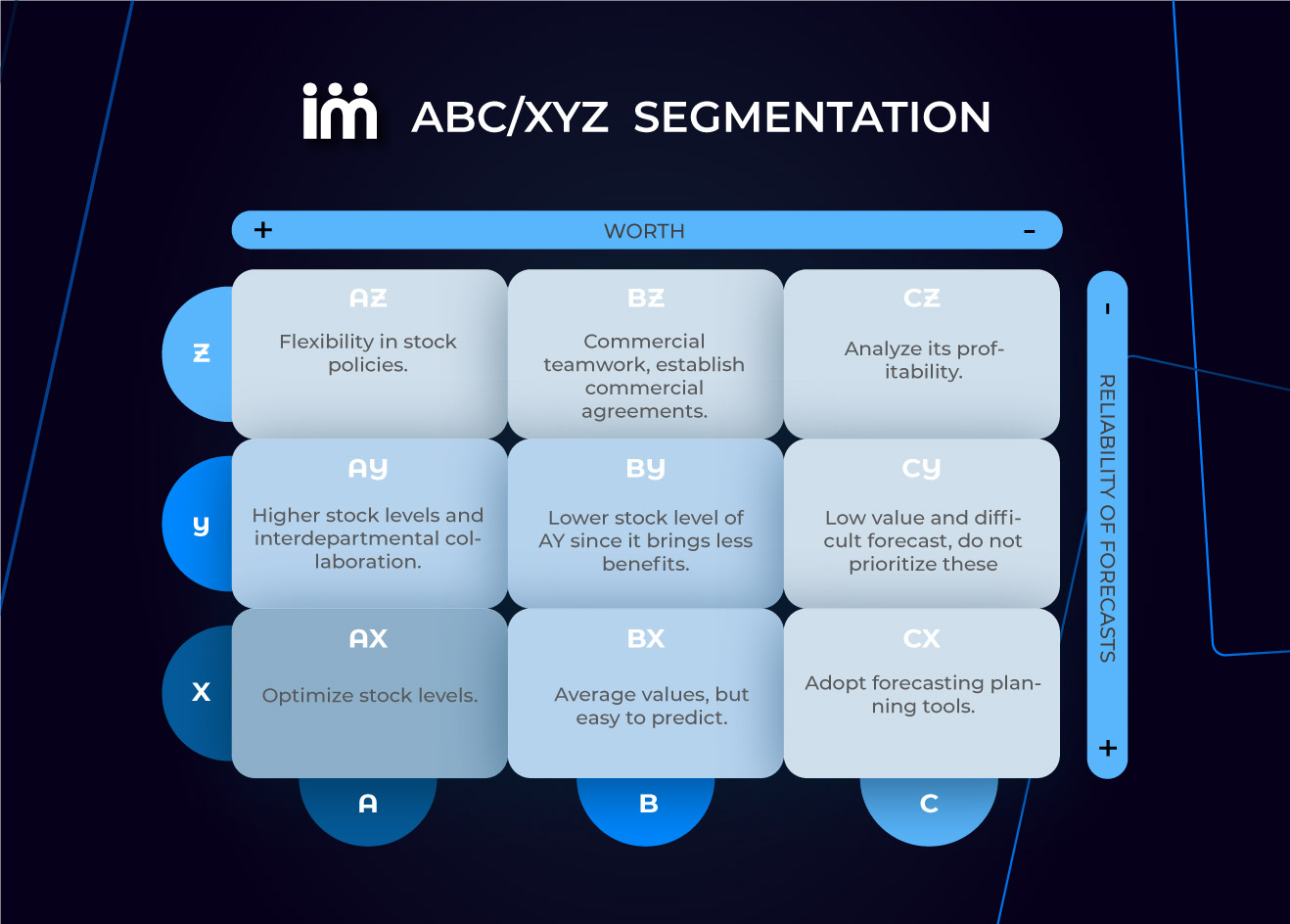
Strategic Actions for Each ABC-XYZ Segmentation Group
Other Considerations for ABC-XYZ Classification
When adapting forecasting and planning strategies according to ABC-XYZ segmentation, efficiency in reference management can be improved, resource allocation optimized, and actions adapted to the specific needs of each group of elements. This contributes to better information management and user satisfaction by offering a service more suited to their needs.
In addition to the recommended actions for each ABC-XYZ segmentation combination, it is important to perform constant monitoring and evaluation of the results obtained. This will allow for assessing the effectiveness of implemented strategies and making adjustments if necessary. Some additional actions to consider include:
- Periodic Update of Segmentation: It is essential to review and update

Enter your email and download the content
In supply chain management, identifying key elements that require special attention can make the difference between success and failure.


