
Demand Planning
Demand planning is an essential component in a company's supply chain management process. This stage of the process involves anticipating and projecting what the company is expected to sell in the future, in other words, the expected demand. To achieve this, it is necessary to determine the estimated demand for each product the company markets and, based on this information, develop strategic plans to efficiently meet that demand.
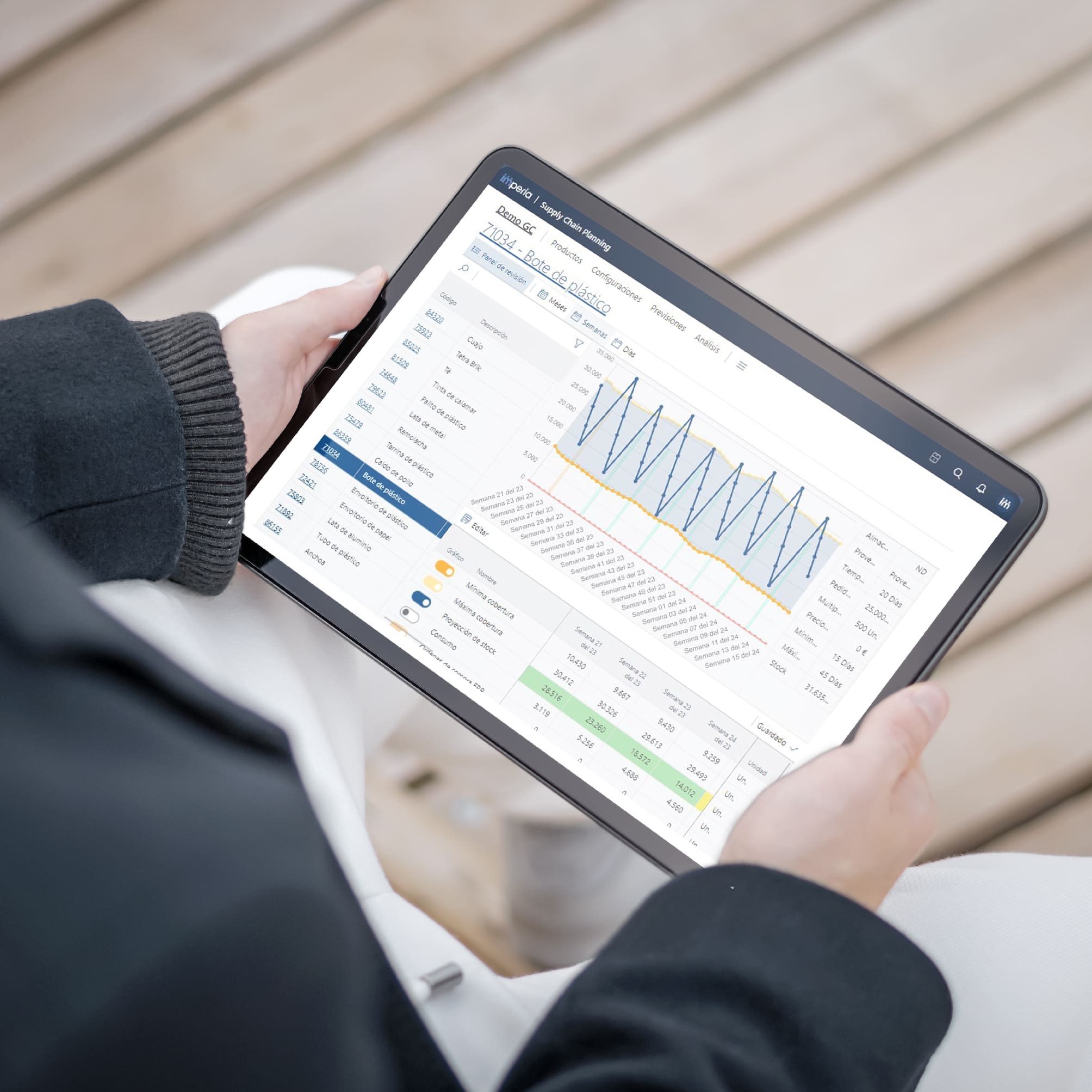
To better understand this concept, let's consider the following scenario: if we represent the current state of a company with a dotted line (as shown in the image below), by analyzing its sales history, we can get an idea of the volume of products sold in the past. However, to ensure that there is enough inventory available to meet the future needs of customers, it will be necessary to master forecasting techniques and accurately anticipate how demand will behave in the future.
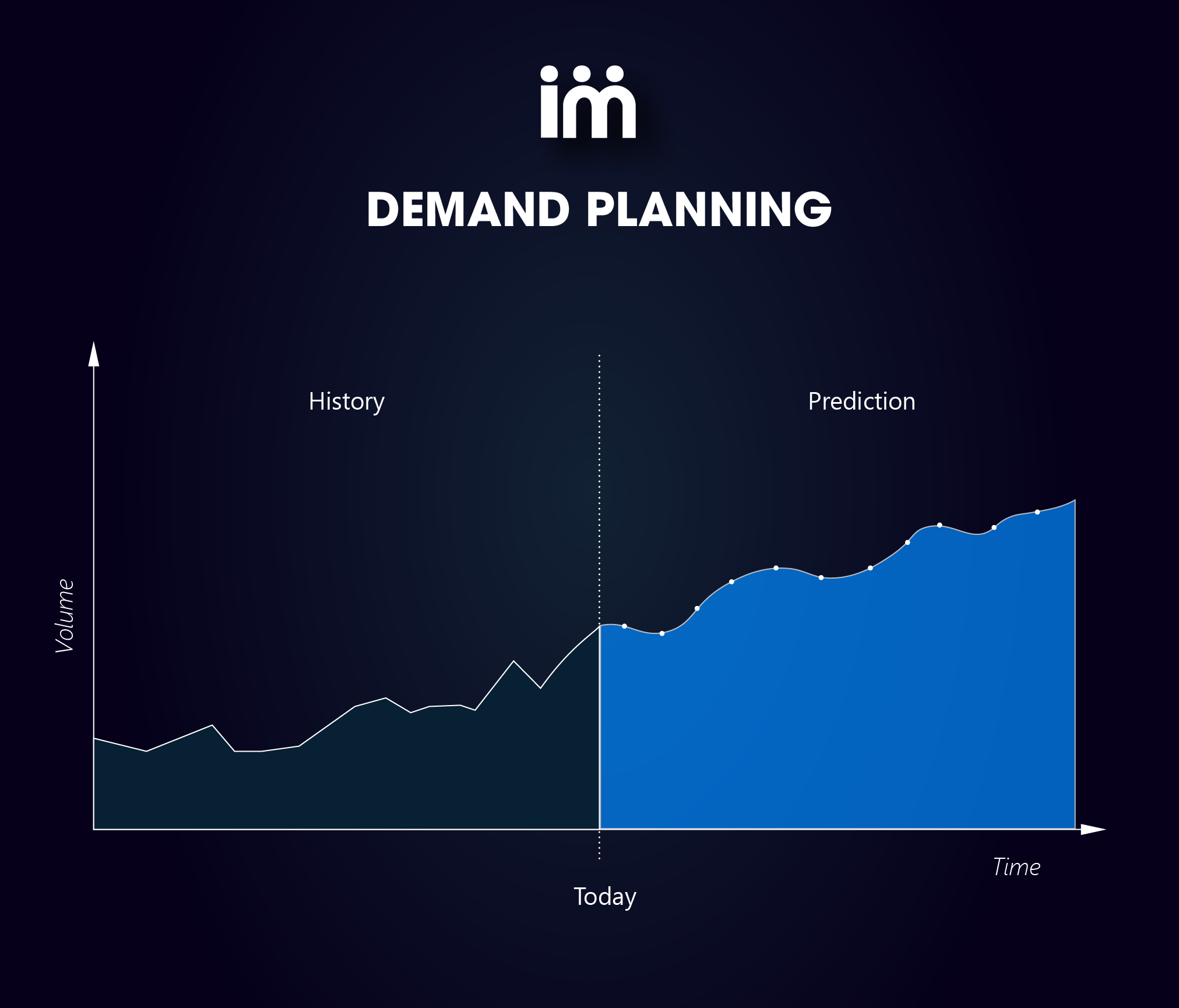
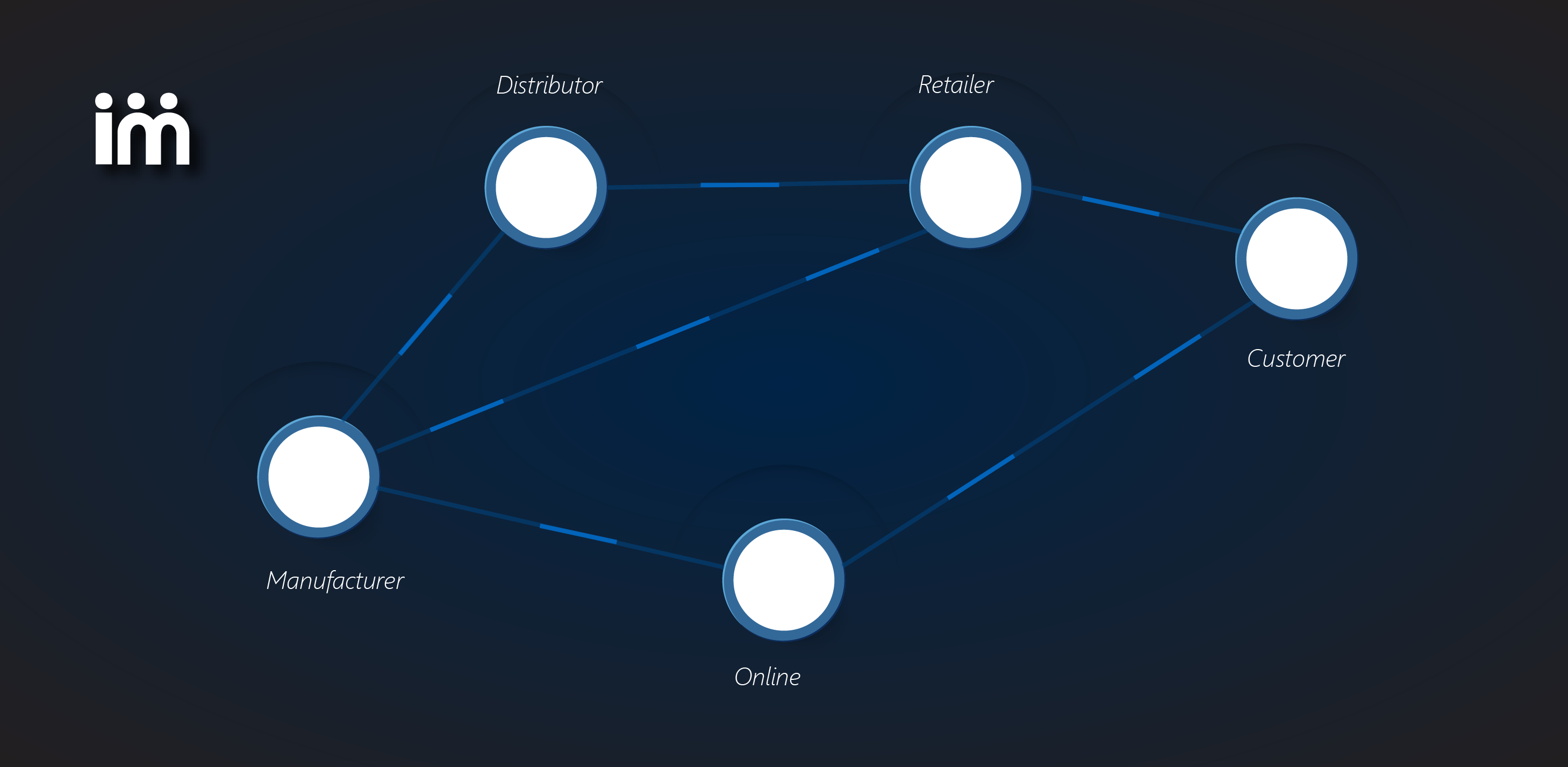
You need to predict what products you plan to sell and how many of them you need to forecast. You must plan where you will sell all these products, through which channels, and how you will process them through your distribution network. Lastly, you will need to determine when they will be sold in the future.
Demand planning is a central activity in the supply chain for many industries and businesses. Whether a company sells products to a B2B or B2C customer base, a demand plan is necessary to determine how much product should be available to meet the demand.

Demand Planning Process
Demand planning is considered a strategic process for most companies. However, too often, developing and executing this process can be a considerable challenge due to its complexity.
The fundamental purpose of this process is to provide planners with a reliable demand plan, whether on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, that they can carry out seamlessly.
Demand planning involves 7 key steps:
- Collect critical information and data;
- Measure the accuracy of a forecast against actual or post-game analysis;
- Develop a baseline forecast (and sometimes an uplift if necessary);
- Provide information to supply chain forecast analysts and planners;
- Edit, review, and validate the forecasts;
- Approve and present a final demand forecast; and
- Archive and prepare for the next forecast cycle.
Why Demand Planning Is Important
Demand planning serves two essential functions:
Firstly, demand forecasting enables companies to visualize their inventory status and ensure they have the right amount of products in the right places, preparing them to effectively meet customer needs. This facilitates more efficient and strategic inventory management.
On the other hand, demand planning also helps avoid the risks associated with excess inventory, which can include high storage costs, the need for price reductions, or the rapid sale of unsold inventory through significant discounts to free up space for new products.
Demand Planning Software
When choosing demand planning software, companies encounter a wide variety of options. The choice of the right software should be based on the specific needs of each company. Demand planners should have a strong understanding of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems as these systems are the primary source of data. Furthermore, it is essential for demand planners to become experts in using demand forecasting software. Demand planning and forecasting are crucial because many factors can affect and shape demand, including economic trends, weather events, and global emergencies.
Successful demand planners play an essential role in a company's supply chain planning strategy. They use internal (analytical, marketing, sales, etc.) and external (weather conditions, economic factors, consumer buying behavior, etc.) data to better estimate the demand for future products. Successful demand planners design a pilot version based on historical data. It's crucial for companies to hire talented demand planners and invest in ongoing demand planning education.
What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the active process of overseeing activities related to the supply chain with the goal of maximizing value for the customer and achieving sustainable competitive advantage. It represents a conscious strategic effort by companies involved in the supply chain to develop and execute their operations as efficiently and effectively as possible. Supply chain activities range from product development and raw material acquisition to production, logistics, and the management of information systems necessary to coordinate all these processes.
A supply chain management system consists of five basic elements:
Supply Chain Planning
To meet customer demands, supply chain managers must plan ahead. This involves forecasting demand, designing the supply chain, and establishing key performance indicators to measure whether the supply chain is performing as expected in terms of efficiency, delivering value to customers, and contributing to organizational goals.
Procurement
The selection of suppliers who will provide goods, raw materials, or services to create the product is a critical component of the supply chain. This includes creating contracts governing suppliers and managing and monitoring existing relationships. As part of strategic procurement, supply chain managers must oversee various processes, including ordering, receiving, inventory management, and vendor billing.
Production
Supply chain managers also play a role in coordinating the production of products, including reviewing/accepting raw materials, manufacturing products, controlling and quality testing, and packaging.
Distribution
Logistics is a significant part of the supply chain because it ensures a product reaches the customer. The logistics process includes coordinating orders, scheduling deliveries, shipping, billing customers, and receiving payments.
Returns
It's also important to create a process for managing product returns. This can include a protocol for disposing of or remanufacturing a faulty product or simply creating a process for returning a product to the original warehouse.
What Is the Difference Between Dependent and Independent Demand?
There are two types of demand: dependent and independent.
If the demand for a product is independent, it means that the demand for that item is driven by market conditions and not necessarily related to production decisions for other products that may be in stock. In manufacturing, products with independent demand are the final product sold to the customer.
The dependent demand for a product is based on the production decisions of its "parent" components. The term "parent" is defined as an item that is manufactured from one or more components. For example, a desk is a parent product composed of components like a tabletop, legs, and furniture fasteners.
Demand planning and management rely on accurate data and collaborative forecasting processes so that companies can reach an agreement (both internally and with external suppliers and sellers) on the expected timing, product mix, and demand locations. The demand planning process is crucial for other processes such as marketing, logistics, and budgeting.
Best Practices in Demand Planning
Understanding and implementing best practices in demand planning can make your processes more effective and lead to more accurate forecasting results.
Important steps include:
- Collecting data and information from relevant departments (sales, marketing, finance, etc.).
- Obtaining stakeholder approval to use statistical models and using collaborative methods to combine the best forecasting data.
- Linking internal information, such as product attributes, inventory data, and safety stocks, to master data management in real-time to ensure that the data is current and accurate.
- Incorporating external data such as weather conditions, economic factors, and consumer buying behavior to drive machine learning solutions.
- Integrating the forecasting process with business planning efforts and making forecasting a recurring process.
The Future of Demand Planning
Advanced algorithms and AI/machine learning (AI/ML) will continue to evolve, being able to collect more data and detect which factors are impacting and shaping demand. This will enable companies to make more informed decisions in all aspects and create resilient supply chains that can mitigate disruptions and capitalize on market growth opportunities. The roles of data scientists and analysts are becoming increasingly critical for companies to leverage the benefits of AI/ML. A Demand Planning team composed of data scientists, analysts, and planners can help create a competitive advantage for organizations.























































 Imperia_thumbnail.jpg)





















