
Optimizing the supply chain involves efficiently adjusting and managing essential capacities and resources at all stages of the process, from production to customer delivery.
Below, we present the essential aspects for the definition of a sound operational strategy, thus allowing for an optimal end-to-end supply chain:
- Demand forecasting.
- Production decisions.
- Inventory management.
- Logistics strategy: storage and transportation.
- Comparative analysis: seeking process optimization while considering industry best practices.
Focusing on improving these factors will enable companies to reduce costs, optimize inventories, and ensure timely product delivery.
Adequate production planning
The initial production process plays a crucial role in the whole chain. Decisions made at this stage reverberate downstream, so it is essential to ensure accurate planning and sound decisions.
For example, when a customer looks for an item in a shop and finds that it is out of stock, the reasons may lie in several points:
- Lack of coordination between the shop and the warehouse, leading to problems in order, stock and transport management.
- Mismatches between the warehouse and the factory.
- Inadequate decisions taken in the production plant.
Incorrect demand forecasting, errors in supplier order management or poor production planning can result in shortages of raw materials or manufacturing delays, thus affecting the availability of the product at the time the customer requires it. Consequently, customer satisfaction is directly affected.
Therefore, the critical starting point lies in production planning that matches future demand. This approach ensures an adequate level of products and makes it possible to anticipate customer needs. The following sequence involves effective logistics planning (storage and transport) and efficient inventory management, thus ensuring that the right product is at the right place at the right time for the customer.
How to achieve effective production planning?
In order to plan production operations correctly, it is crucial to consider a number of factors presented below:
1. Accurate forecasting of demand:
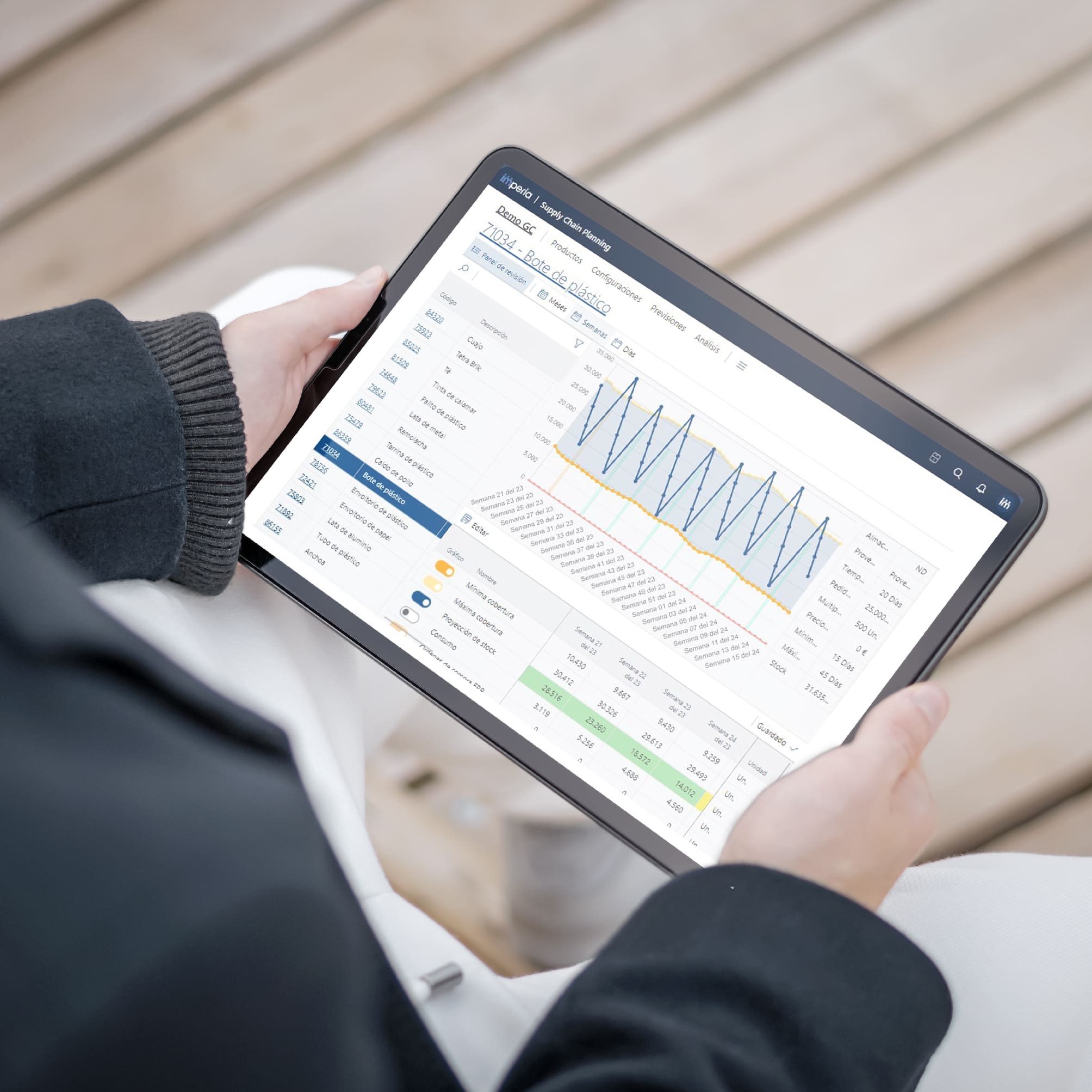
In an environment where market volatility and changing buying patterns are the norm, implementing advanced demand forecasting methods becomes essential in virtually every industry. Demand forecasting reduces inventory levels, synchronises the flow between sales and operations, and increases customer satisfaction. The benefits include:
- Obtain a clear view of projected cash flow and production capacity needs.
- Identify market trends.
- Use from basic forecasting approaches, such as time series, to more complex causal models that consider multiple factors.
2. Sales and operations planning:
Alignment between production, sales and logistics is crucial. Scenarios must be created based on demand forecasts, production constraints, inventory costs and marketing campaigns. These scenarios are compared with the company's overall objectives to:
- Generate diverse scenarios based on sales and/or production constraints.
- Optimise integrated inventory management.
- Display a KPI dashboard covering all relevant financial KPIs.
3. Master production planning:
The Master Production Plan strikes a balance between production capacity and incoming orders. By linking limited resources and agreed delivery dates, it ensures efficient use of available capacity and high delivery performance. This allows:
- Accept orders and commit delivery dates in real-time.
- Balance between Make-to-Order (MTO) and Make-to-Stock (MTS) manufacturing to minimize inventory levels.
- Fulfill all orders completely and punctually.
- Ensure adequate supply of materials.
4. Scheduling of production operations:
Demand-optimised schedules can be generated, taking into account all relevant constraints and parameters. This ensures timely and complete delivery of orders. Scheduling can be a combination of decision support and full automation.
- The ramifications of any planning decision are instantly visible.
- A comprehensive dashboard of KPIs allows evaluating the quality of planning.
- Automatic material allocation.
5. Real-time replanning:
Last minute orders, process interruptions, raw material shortages or other unforeseen events demand immediate, real-time replanning of the production process.
- Manual replanning can lead to production or capacity problems further down the chain.
- Automatic and complete replanning considers all possible consequences, generating a fine-tuned plan that minimises disruptions.
In summary, optimizing the supply chain begins with careful production planning, as the decisions made in this phase impact every subsequent link. The fundamental pillars for establishing a robust operational strategy are accurate demand forecasting, coordination between sales and operations, master production planning, optimal scheduling of operations, and the ability to adapt in real-time.
By focusing on improving these aspects, companies can reduce costs, optimize inventories, and ensure the timely delivery of products. Proper production management becomes the foundation that allows building a smooth and efficient supply chain, bringing satisfaction to both customers and business goals.























































 Imperia_thumbnail.jpg)





















